The Goal of Restructuring:
The goal of restructuring via M&A analysis depends on the purpose of the M&A. What the organization need you are trying to fulfill, for example:
- If the goal is complementary, then you are looking at differences to expand your reach.
- If the goal is economics of scale, then you are looking at similarities to reduce costs or keep a competitor out of the market.
Analysis for Success
Key analytics are needed to investigate the probability of success of the restructure effort. Here is a short list of new and emerging analytics that provide insight necessary for success:
- Comparative analysis of core operational components and organization direction
- Relationship analysis between the structural factors
- Property analysis of the lists of component members
- Multi criteria subjective, objective and hybrid decision analysis
- Enhanced access to new customer segments
Achieving the synergy of a restructuring such as a merger or acquisition requires learning to navigate the unknown and anticipate the future environment. This creates a better set of change options for the organization and identifies a path to adaptation.
Increase the Probability of M&A success
Improve insight on operations using more objective analysis.
Benefits of M&A
Benefits that accrue from an M&A initiative are:
- Increased market share and competitive positioning.
- Cost savings through synergies.
- Expanded product and service offerings.
- Accelerated growth opportunities.
- Enhanced access to new customer segments
Barriers to Structural Change Success
There are several potential and barriers to success of any restructuring initiative especially mergers and acquisitions. These barriers especially culture and synergies account for the bulk of failures.
- Cultural integration challenges.
- Overestimation of synergies.
- Regulatory and compliance hurdles.
- Retention of key talent post-merger.
- High execution complexity and cost.
What to Investigate for an M&A effort
An investigation of operations for compatibility, or at least exposing the issues involved requires comparative analysis and relationship analysis for hidden, enabling and barrier types of factors is needed. Here is a core set of categories/lists of 5 management concerns:
- Strategies
- Capabilities
- Core Processes
- Core Applications
- Core Data Bases
In addition a basic culture assessment is useful to identify resistance points to an structural change.
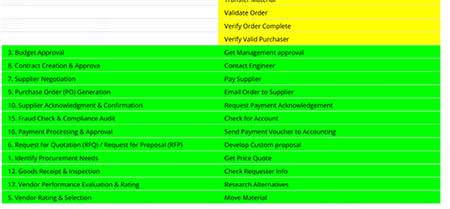
A key analytical technique is a composite ranking of multi criteria decision making. In this case an example of using subjective criteria from 2 organizations related to their strategies. The idea is to determine if they have a compatible view of strategic direction.
Some interpretive comments are in order:
- Note that Organization 1 is more detailed than 2, also, 2 has more general process steps indicating it is most likely a parent process. The follow on task is to make sure the processes are at the same level in the process hierarchy to do the ranking analysis.
- Also, what appears significant in the ranking is that the ranking of Organization 1 is not the same as Organization 2, meaning a more difficult integration effort.
- Organization 2 has double verbs in several of the process steps. These should be separated into discrete actions. All this is part of process model cleanup.
- The comparison analysis also lists those elements in each model that are only in 1, only in 2 or in both models. A sliding scale of comparison is used in this case set at 33%, not a high benchmark for determining similar processes. A value of 50% or more is better. However, the result here is an indication of the degree of effort to integrate the 2 processes.
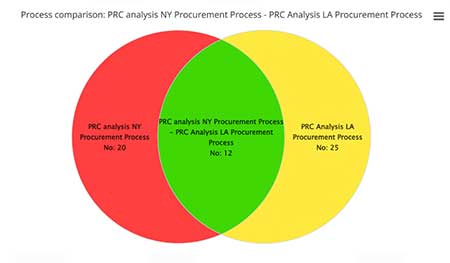
Another way to view the result is via a simple Venn diagram. Here you see that 12 steps have things in common , 20 steps in process 1 are not in the intersection ad 23 from process 2 are no in the intersection.
Further analysis using neural nets and correlation matrices can easily be done to get alternative added insights from the data.